概述
HBase:Hadoop Database
- 一种在Hadoop之上的NoSQL 的Key/vale数据库,适合实时查询
- 利用Hadoop HDFS作为其文件存储系统
- 利用Hadoop MapReduce来处理其海量数据
- 利用Zookeeper作为协调工具
- 是一个高可靠性、高性能、面向列、可伸缩的分布式存储系统
- 适合海量数据(如20PB)的秒级简单查询的数据库
- 适合key-value查询
- 适合按时间排序top n的场景
- 适合大量读写
数据模型
数据模型
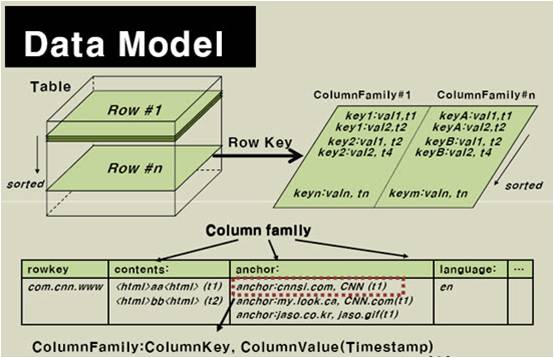
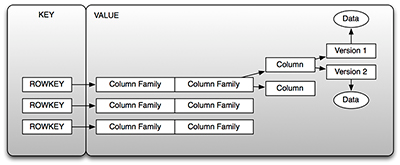
- Table:存储管理数据
RowKey:行键(类似于关系型数据库中的主键)ColumnFamily:列族(定义表时指定),可包含任意多个列(插入记录时动态增加)Cell:单元格,由{rowKey,columnFamily:columnName}确定的存储单元- 可存储一份数据的多个版本,由
Timestamp(时间戳)属性区分,即数据具有版本特性 - 由
{rowKey, columnFamily:columnName, version}可确定某一版的Data - 若不指定时间戳或者版本,默认取最新的数据
- 可存储一份数据的多个版本,由
逻辑数据模型
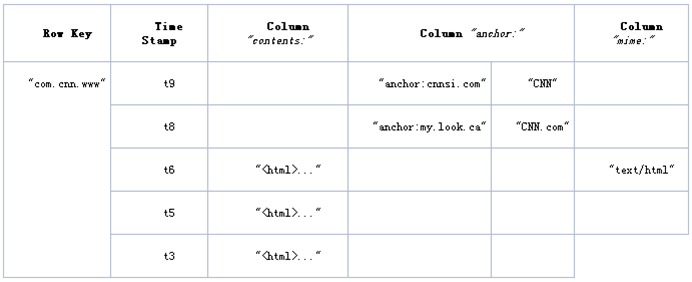
物理数据模型
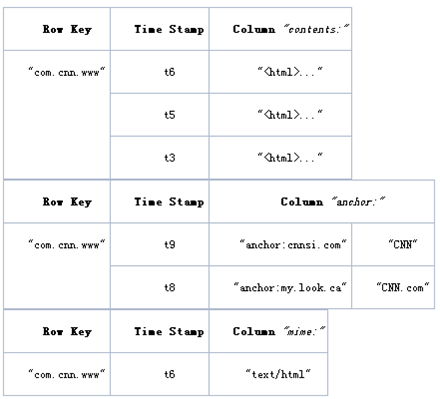
说明:
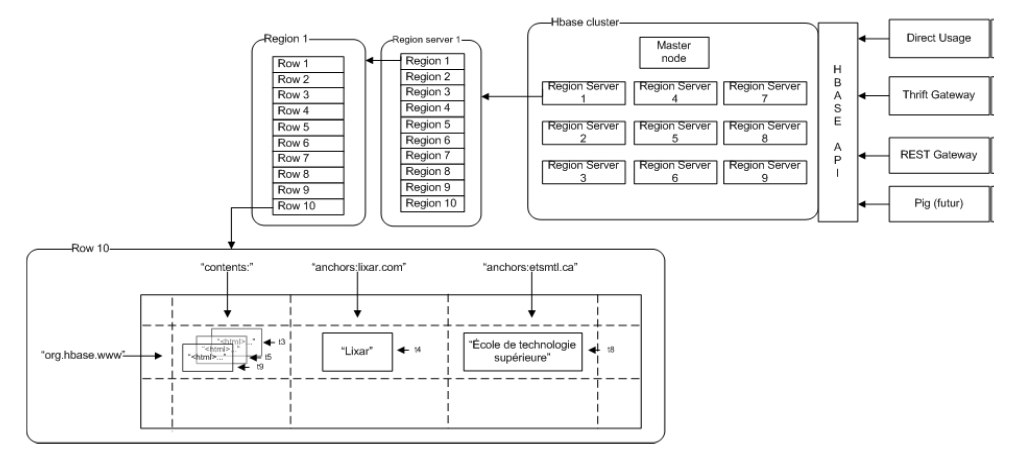
- 存储划分:
Table按RowKey范围[startKey,endKey)划分成N个Region- 各个
Region分散存储在不同的RegionServer(单独的物理机器)中 - 这样对表的操作转化为对多台
RegionServer的并行操作
- 各个
Region按ColumnFamily一对一划分成Store,每个store包括:MemStore内存存储 (先,达到阀值后,写入StoreFile)StoreFile文件存储(对应一个HFile,存放在Hadoop HDFS)
- 存储结构:
RowKey,ColumnName按字典顺序物理存储Timestamp是一个64位整数- 所有数据以
byte[]存储
- 存储划分:
架构体系
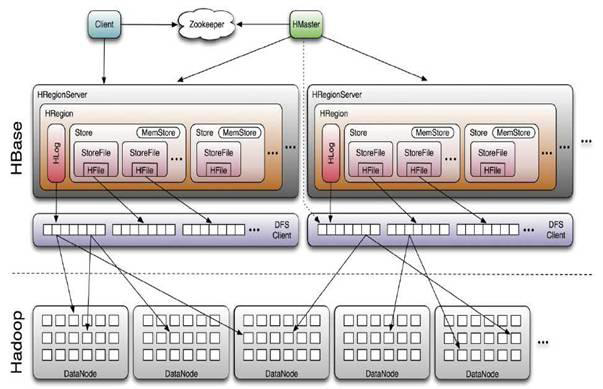
主从式结构
- Master(主):可以启动多个,由Zookeeper的Master Election机制保证总有一个Master运行
- 管理RegionServer
- 分配Region
- RegionServer(从):一个物理节点一个
- 存储Region
- 响应用户I/O请求,向HDFS文件系统中读写数据
- 合并切分Region(StoreFile)
- Zookeeper(协调)
- 保证集群中只有一个Running Master
- 监控RegionServer的状态,实时通知给Master
- 存储HBase的Schema(包括有哪些Table,每个Table有哪些ColumnFamily)
- 存储Region寻址入口(即
-ROOT-表的location)
- 保证集群中只有一个Running Master
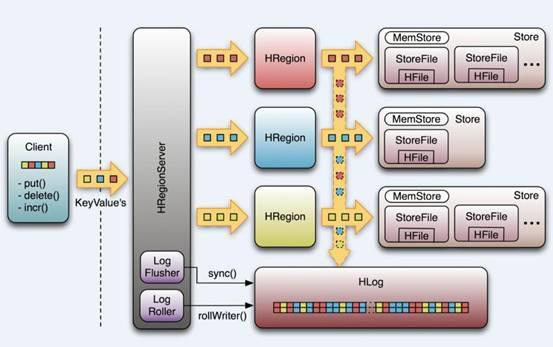
HRegion 进程:
- HLog :预写式日志(所有更新操作先记录进日志,再操作),用于做灾难恢复Failover
- Store :每个Store存放一个列族
- MemStore 内存存储 (先,达到阀值后,写入StoreFile)
- StoreFile 文件存储(对应一个HFile,存放在Hadoop HDFS)
- 每次写入就形成一份单独的
- 数量增长到一定阀值:合并StoreFile(合并时会进行版本合并和删除工作)-- HDFS适合存储大文件
- 大小超过一定阀值:分割当前Region(再由HMaster分配到其他RegionServer)-- 实现负载均衡
- 每次写入就形成一份单独的
注意:
- HBase中有两张特殊的Table(
-ROOT-和.META.).META.:记录了用户表的Region信息,.META.表本身可划分成N个regoin-ROOT-:记录了.META.表划分成的N个Region的信息,-ROOT-本身只有一个,不划分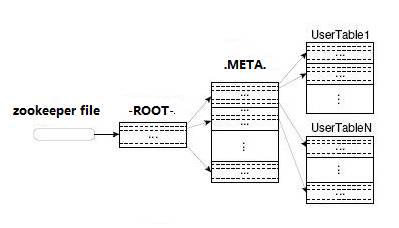
- Client访问HBase上数据数据(并不需要master参与):
zookeeper=>-ROOT-表=>.META.表=>Region位置=>访问 - Client包含访问HBase的接口,可通过维护着一些cache来加快对HBase的访问(比如缓存region的位置信息)
安装
伪分布式
- 下载解压安装包
- 设置环境变量(
/etc/profile文件)HBASE_HOMEPATH
- 配置(
$HBASE_HOME/conf目录下)hbase-env.shexport JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk # 使用HBase内置的Zookeeper export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=truehbase-site.xml<property> <name>hbase.rootdir</name> <value>hdfs://hadoop0:9000/hbase</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.cluster.distributed</name> <value>true</value> </property> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>hadoop0</value> </property> <property> <name>dfs.replication</name> <value>1</value> </property>
- 启动
- 运行Hadoop
- 运行HBase:
start-hbase.sh
- 验证
jps三个进程:HMaster、HRegionServer、HQuorumPeerhttp://hadoop0:60010
集群式
(在原来的hadoop0上的hbase伪分布基础上进行搭建)
例如:
- Master:hadoop0
RegionServer:hadoop1,hadoop2
配置(
$HBASE_HOME/conf目录下)hbase-env.shexport JAVA_HOME=/usr/local/jdk # 不使用HBase内置的Zookeeper export HBASE_MANAGES_ZK=falsehbase-site.xml... <!-- 配置Zookeeper监控管理的节点(hostname)--> <property> <name>hbase.zookeeper.quorum</name> <value>hadoop0,hadoop1,hadoop2</value> </property>regionservers(配置RegionServer的hostname)hadoop1 hadoop2
- 复制配置好的hbase到其他节点
scp -rp ./hbase `hadoop`@hadoop1:~ scp -rp ./hbase `hadoop`@hadoop2:~ - 启动
- 运行Hadoop
- 运行zookeeper
- 运行HBase:
start-hbase.sh
操作
注意:HBase不能支持where条件、Order by 查询,只支持按照Row key来查询,但是可以通过HBase提供的API进行条件过滤
Shell Cmd
- 启用HBase Shell命令行
> hbase shell ... > quite - 常用命令
名称 命令表达式 创建表 create '表名称', '列族名称1','列族名称2','列族名称N' 添加记录 put '表名称', '行键', '列族名称:列名称', '值' 查看记录 get '表名称', '行键' 查看表中的记录总数 count '表名称' 删除记录 delete '表名' ,'行键' , '列名称' 删除一张表 先要屏蔽该表,才能对该表进行删除,第一步 disable '表名称' 第二步 drop '表名称' 查看所有记录 scan "表名称" 查看某个表某个列中所有数据 scan "表名称" , {COLUMNS=>'列族名称:列名称'} 更新记录 就是重写一遍进行覆盖 - 注意:
- HBase其实没有delete操作,只有insert,以Timestamp区分新旧记录
- 为充分利用分布式,可使用reverse key,hash,复合行键等技巧改造行键
- 行键打乱后,可更均匀随机的分配到各节点,而不是集中在一个节点
操作示例:
表操作:
- 创建表
> create 'users','user_id','address','info' - 查看表
> list > describe 'users' - 验证表
> exists 'users' > is_enabled 'users' > is_disabled 'users' - 删除表
> disable 'users' > delete 'users'
- 创建表
记录操作:
- 插入
> put 'users','xiaoming','info:age','24'; > put 'users','xiaoming','info:birthday','1987-06-17'; > put 'users','xiaoming','info:company','alibaba'; > put 'users','xiaoming','address:contry','china'; > put 'users','xiaoming','address:province','zhejiang'; > put 'users','xiaoming','address:city','hangzhou'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','info:birthday','1987-4-17'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','info:favorite','movie'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','info:company','alibaba'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','address:contry','china'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','address:province','guangdong'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','address:city','jieyang'; > put 'users','zhangyifei','address:town','xianqiao'; 查询
> get 'users','xiaoming' > get 'users','xiaoming','info' > get 'users','xiaoming','info:age' # 获取单元格数据的版本数据 > get 'users','xiaoming',{COLUMN=>'info:age',VERSIONS=>1} > get 'users','xiaoming',{COLUMN=>'info:age',VERSIONS=>2} > get 'users','xiaoming',{COLUMN=>'info:age',VERSIONS=>3} # 获取单元格数据的某个版本数据 > get 'users','xiaoming',{COLUMN=>'info:age',TIMESTAMP=>1364874937056} # 全表扫描 > scan 'users' # 统计表的行数 > count 'users'- 更新
> put 'users','xiaoming','info:age' ,'29' > get 'users','xiaoming','info:age' 删除
# 删除某列值 > delete 'users','xiaoming','info:age' # 删除整行 >deleteall 'users','xiaoming' # 清空 > truncate 'users'
- 插入
Java API
依赖包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-client</artifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}</version>
</dependency>
使用示例:
Configuration conf = HBaseConfiguration.create();
conf.set("hbase.rootdir", "hdfs://hadoop0:9000/hbase");
//使用eclipse时必须添加这个,否则无法定位
conf.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop0");
HBaseAdmin admin = new HBaseAdmin(conf);
String tableName="users";
String columnFamily="info";
// 1. 创建一张表
if (admin.tableExists(tableName)) {
System.out.println("table exists!");
}else{
HTableDescriptor tableDesc = new HTableDescriptor(tableName);
tableDesc.addFamily(new HColumnDescriptor(columnFamily));
admin.createTable(tableDesc);
System.out.println("create table success!");
}
// 2. 添加一条记录
String rowKey="xiaoming";
String column="age";
String data="24";
HTable table = new HTable(conf, tableName);
Put p1 = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
p1.add(Bytes.toBytes(columnFamily), Bytes.toBytes(column), Bytes.toBytes(data));
table.put(p1);
System.out.println("put'"+rowKey+"',"+columnFamily+":"+column+"','"+data+"'");
// 3. 读取一条记录
Get get = new Get(Bytes.toBytes(rowKey));
Result result = table.get(get);
System.out.println("Get: "+result);
// 4. 显示所有数据
Scan scan = new Scan();
ResultScanner scanner = table.getScanner(scan);
/*scan.setStartRow(Bytes.toBytes("134/"));
scan.setStopRow( Bytes.toBytes("134:"));
scan.setMaxVersions(1);*/
for (Result res : scanner) {
System.out.println("Scan: "+res );
}
table.close();
// 5. 删除表
if(admin.tableExists(tableName)){
try {
admin.disableTable(tableName);
admin.deleteTable(tableName);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Delete "+tableName+" 失败");
}
}
admin.close();
System.out.println("Delete "+tableName+" 成功");
结合MapReduce操作
Hbase对Mapreduce API进行了扩展,方便Mapreduce任务读写HTable数据
| HBase MapReduce | Hadoop MapReduce |
|---|---|
| org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableMapper | org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Mapper |
| org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableReducer | org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.Reducer |
| org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableInputFormat | org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputFormat |
| org.apache.hadoop.hbase.mapreduce.TableOutputFormat | org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.OutputFormat |
依赖包:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.hbase</groupId>
<artifactId>hbase-server</artifactId>
<version>${hbase.version}</version>
</dependency>
使用示例1:统计
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration config = HBaseConfiguration.create();
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop0");
Job job = new Job(config,"HBaseTotal");
job.setJarByClass(TotalOnHBase.class);
Scan scan = new Scan();
scan.setCaching(500);
scan.setCacheBlocks(false);
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableMapperJob("access-log",scan,MyTableMapper.class,Text.class,IntWritable.class,job);
TableMapReduceUtil.initTableReducerJob("total-access",MyTableReducer.class,job);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
public class MyTableMapper extends TableMapper<Text, IntWritable> {
private final IntWritable ONE = new IntWritable(1);
private Text text = new Text();
public void map(ImmutableBytesWritable row, Result value, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
String ip = Bytes.toString(row.get()).split("-")[0];
String url = new String(value.getValue(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("url")));
text.set(ip+"&"+url);
context.write(text, ONE);
}
}
public static class MyTableReducer extends TableReducer<Text, IntWritable, ImmutableBytesWritable> {
public void reduce(Text key, Iterable<IntWritable> values, Context context) throws IOException, InterruptedException {
int sum = 0;
for (IntWritable val : values) {
sum += val.get();
}
Put put = new Put(key.getBytes());
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("count"), Bytes.toBytes(String.valueOf(sum)));
context.write(null, put);
}
}
使用示例2:批量导入(TableOutputFormat,TableReducer)
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final Configuration configuration = new Configuration();
//设置zookeeper
configuration.set("hbase.zookeeper.quorum", "hadoop0");
//设置hbase表名称
configuration.set(TableOutputFormat.OUTPUT_TABLE, "wlan_log");
//将该值改大,防止hbase超时退出
configuration.set("dfs.socket.timeout", "180000");
final Job job = new Job(configuration, "HBaseBatchImport");
FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, "hdfs://hadoop0:9000/input");
job.setInputFormatClass(TextInputFormat.class);
job.setMapperClass(BatchImportMapper.class);
job.setMapOutputKeyClass(LongWritable.class);
job.setMapOutputValueClass(Text.class);
//BatchImportReducer extends TableReducer
job.setReducerClass(BatchImportReducer.class);
//不再设置输出路径,而是设置输出格式类型
job.setOutputFormatClass(TableOutputFormat.class);
job.waitForCompletion(true);
}
// BatchImportMapper 数据清理,省略...
// BatchImportReducer 将数据写入HBase
public class BatchImportReducer extends TableReducer<LongWritable, Text, NullWritable>{
protected void reduce(LongWritable key, Iterable<Text> values,Context context) throws IOException ,InterruptedException {
for (Text text : values) {
final String[] splited = text.toString().split("\t");
final Put put = new Put(Bytes.toBytes(splited[0]));
put.add(Bytes.toBytes("info"), Bytes.toBytes("age"), Bytes.toBytes(splited[1]));
//省略其他字段,调用put.add(....)即可
context.write(NullWritable.get(), put);
}
};
}