Starter
文档型数据库: 一条记录就是一个文档,由字段和值对组成(BSON)
官网 | Doc | 中文社区 | Github | Jira (bug fix)
特性:
- 无数据结构限制(每条记录可以有完全不同的结构)
- 完全的索引支持(单键/多键索引,复合索引,全文索引,地理位置索引)
- 丰富的查询语言(Shell内置javascript引擎可以直接执行JS代码)
- 方便的冗余和扩展(复制集Replica Set:保证数据安全,高可用性,分片Sharding:水平扩展数据规模)
- 插件化的存储引擎支持(WiredTiger, MMAPv1, In-Memory, Encrypted, 3rd Party Engine)
- WiredTiger(存储引擎):
- MongoDB3.2 之后的默认存储引擎
- 拥有效率非常高的缓存机制
- 支持在内存中和磁盘上对索引进行压缩(压缩时使用了前缀压缩的方式以减少RAM的使用)
- 能够保证对于同一个文档的操作都是原子的,任意一个写操作都不能原子性地影响多个文档或者多个集合
- WiredTiger(存储引擎):
使用:
- CRUD -> 索引创建和使用 -> 复杂聚合查询 -> 数据集分片,在不同分片间维持数据均衡 -> 数据备份和恢复 -> 数据迁移
部署:
- 单机 -> 拥有冗余容错功能的复制集 -> 分片大规模数据集群(横向扩展,自动分片,轻松支持TB-PB数量级) -> 集群的自动部署
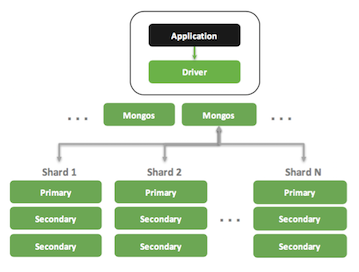
- 单机 -> 拥有冗余容错功能的复制集 -> 分片大规模数据集群(横向扩展,自动分片,轻松支持TB-PB数量级) -> 集群的自动部署
数据模型
RelationDB vs. MongoDB :
- RelationDB:
- Table -> Record -> field & value
- MongoDB:
- Collection -> Document -> key & value
- 表示文档间关系的方式:
Reference引用:标准化的数据模型,可通过某个引用值链接到其他文档(与 MySQL 的外键非常相似,但不会对引用的对象是否真正存在做出任何的约束)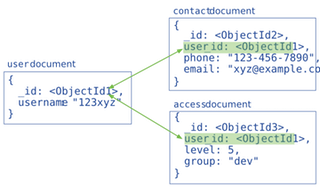
Embedded Data嵌入:非标准化的数据模型,相关联的数据保存在同一个文档结构之内
- 注:MongoDB不对Collection的数据结构进行限制,但在实际使用中,尽量同一个Collection中的文档具有类似的结构
搭建MongoDB测试环境
这里直接使用Docker搭建MongoDB测试环境
- 搜索下载mongo image
$ docker search mongo $ docker pull mongo 启动一个容器(micro-mongo)作为mongo server
# 建一个单独的数据卷store-mongo (为防止docker machine重启后数据丢失) $ docker create --name store-mongo mongo # 创建启动一个container as mongo server : micro-mongo,并挂载数据卷store-mongo $ docker run --volumes-from store-mongo --name micro-mongo -p 27017:27017 -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_USERNAME=mongoadmin -e MONGO_INITDB_ROOT_PASSWORD=123456 -d mongo:latest # 检查 $ docker ps $ docker log- 使用:
- 方式一:直接进入刚才创建的mongo server容器(micro-mongo)
$ docker exec -it micro-mongo /bin/bash root@480e8bf33600:/# mongo -u mongoadmin -p 123456 --authenticationDatabase admin > show dbs admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB demo 0.000GB local 0.000GB - 方式二:启动一个容器(mongo)作为mongo client连接刚才的micro-mongo
$ docker run -it --rm --link micro-mongo:mongod --name mongo-client mongo:latest mongo -host mongod -u mongoadmin -p 123456 --authenticationDatabase admin demo > show dbs admin 0.000GB config 0.000GB demo 0.000GB local 0.000GB - 方式三:客户端工具 MongoDB Compass
- 方式一:直接进入刚才创建的mongo server容器(micro-mongo)
- 导入测试数据
# load(filename): Loads and runs a JavaScript file into the current shell environment > load("testData.js")
Server/Client
Server: 启动服务,使用命令
mongod$ vi conf/mongod.conf port = 12345 dbpath = data logpath = log/mongod.log fork = true $ mongod -f conf/mongod.confClient: 连接数据库,使用命令
mongo$ mongo --help $ mongo localhost:12345/testdb > use admin > db.shutdownServer()
Mongo Shell
MongoDB的Shell内置javascript引擎可以直接执行JS代码
# 列出所有可用db
show dbs
# 查看当前正在使用的db
db
# 切换当前数据库上下文,即切换当前使用db
# Note:可以切换到一个不存在的db,后面执行db.<collection>.insert(...)操作时会自动创建
use <database>
# 查看当前db的集合集(table)
show collections
show tables
# 格式化打印结果
db.myCollection.find().pretty()
# 无格式打印
db.myCollection.print()
# JSON格式打印
db.myCollection.printjson()
# 多行操作
# 代码行以 '(','{','[' 结束,则随后一行将以省略号 "..." 开始,直到输入对应的')','}',']'
if(x>0){
...count++;
...print(x);
...}
# Tab命令补全
# 例如下面 <Tab> 补全后将列出各种以‘c’开头的方法
db.myCollection.c<Tab>
ACID
| 事物特性 | MongoDB | MySQL (InnoDB) |
|---|---|---|
| 原子性 Atomicity | 单行/文档级原子性 | 多行原子性 |
| 一致性 Consistency | 强一致或最终一致 | 强一致 |
| 隔离性 Isolation | 提交读 | 可重复读 |
| 持久性 Durability | 日志及复制 | 日志 |
原子性 Atomicity
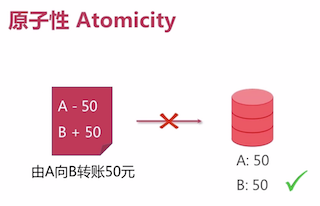
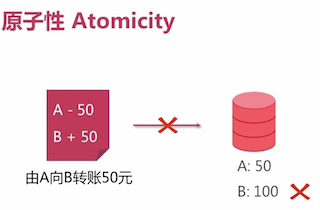
- 支持: 单行/文档级原子性
db.users.update({ username:"Tom"},{$set:{salary:5000}}); - 尚不支持(4.0以下): 多行/多文档/多语句原子性
db.users.update({ salary:{$lt:5000}},{$set:{salary:5000}});- 开始状态:
username salary James 3000 Tom 4000 Melody 4500 Frank 2500 Kelly 3500 Lucy 7600 - 结束状态:中间出错(eg:宕机)
username salary James 5000 Tom 5000 Melody 5000 Frank 2500 <- 宕机 Kelly 3500 Lucy 7600
- 开始状态:
一致性 Consistency
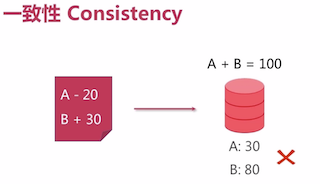
多文档一致性处理:
- 通过建模来避免
- 二阶段提交
- 记录日志,人工干预
注:
- 传统数据库:规则校验主外键
- 分布式数据库:多节点数据一致(Read your writes)
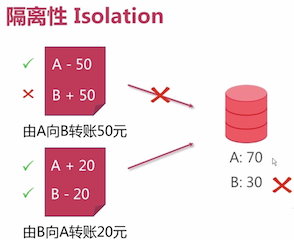
隔离性 Isolation
| Isolation Level | Default Setting |
|---|---|
| Serializable | / |
| Repeatable Read | MySQL |
| Read Committed | PostgreSQL,Oracle |
| Read UnCommitted | MongoDB |
持久性 Durability
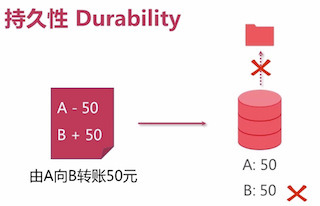
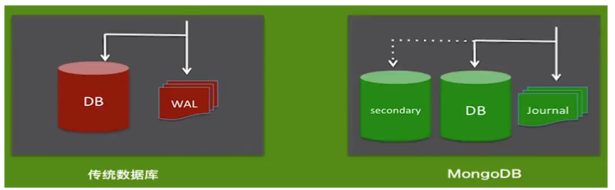
- 机制:
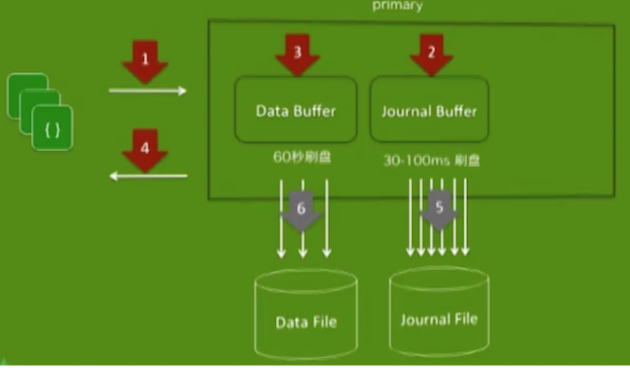
- MongoDB单节点写操作
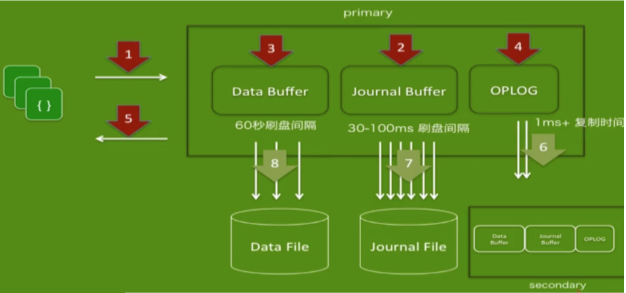
- MongoDB多节点写操作
写关注机制 WriteConcern
{ w: <value>, j: <boolean>, wtimeout: <number> }
- 用来指定mongoDB对写操作的回执行为
- 可在`connection level`或者`写操作level`(insert/update/delete操作的最后一个参数)指定
- 支持以下值:
w: 0/1/n/majority/tagj: true/false 或 0/1wtimeout: millis -- only applicable forw>1
具体:
w: write acknowledgement instancew:0Unacknowledged (无任何回执)- 2.2及以前版本的默认行为
- 网络丢包,系统崩溃,无效数据(早期版本丢数据之罪魁祸首)
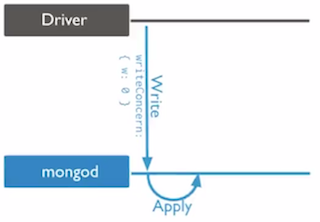
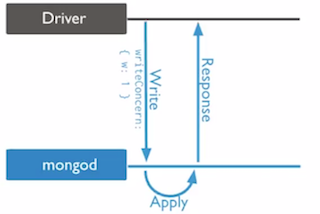
w:1Acknowledged (Mongod在写完内存后返送确认)- 2.4版本以后的默认行为
- 能够处理网络故障,无效数据等错误状态
- 系统崩溃时可能会丢失最多100ms数据
w:2/n/majorityReplica Acknowledged (等待数据复制到n个/大部分节点后再发送回执)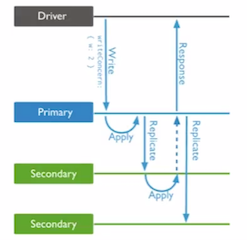
j: journal(恢复日志)- 用于系统宕机时恢复内存数据,保证MongoDB中数据的持久性,
journal与检查点Checkpoint协作:- 在数据文件中查找上一个Checkpoint标识符;
- 在 journal 日志文件中查找Checkpoint标识符对应的记录;
- 重做对应记录之后的全部操作;
- 刷盘间隔:
- MMAP: 30~100ms
- WiredTiger: 100MB/Checkpoint
- eg: 每隔
60s或在journal文件数据的写入达到2GB时设置一次检查点Checkpoint
- 默认为异步刷盘,可用
j:1强制同步刷盘 j:1/trueJournaled,强制 journal 文件的同步 (Journal刷盘后再发送写回执)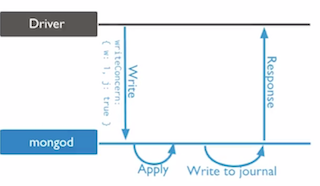
- 用于系统宕机时恢复内存数据,保证MongoDB中数据的持久性,
示例:
场景:插入一些无效数据(eg:10个document同一个
_id),检查实际插入数据数目不使用写关注
{w:0}: 未报错,本以为是10条记录但却显示1条记录> db.test.count() 0 > for(var i=0;i<10;i++){ var res=db.test.insert({_id:10,a:i},{writeConcern:{w:0}}) if(!res.getWriteError()) print("Inserted doc #"+(i+1)); else print(res.getWriteError().errmsg); } Inserted doc #1 Inserted doc #2 Inserted doc #3 Inserted doc #4 Inserted doc #5 Inserted doc #6 Inserted doc #7 Inserted doc #8 Inserted doc #9 Inserted doc #10 > db.test.count() 1 # 期望值为10指定写关注
{w:1}(2.4以后版本默认为1) : 会acknowledge写错误,返回给客户端,最后显示1条记录> db.test.count() 0 > for(var i=0;i<10;i++){ var res=db.test.insert({_id:10,a:i},{writeConcern:{w:1}}) if(!res.getWriteError()) print("Inserted doc #"+(i+1)); else print(res.getWriteError().errmsg); } Inserted doc #1 E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } E11000 duplicate key error index: test.test.$_id_ dup key: { : 10.0 } > db.test.count() 1 # 期望值为1
场景:系统崩溃导致数据丢失(eg:
w:1高速持续写入数据,kill -9 mongod强制关闭mongo服务,然后重新启动mongo检查程序汇报写入的数据和实际插入的数据)function journalDataLoss(journal){ var count=0,start=new Date(); try{ var docs=[]; for(var i=0;i<1000;i++) docs.push({a:i}); while(true){ var res=db.test.insert(docs,{writeConcern:{j:journal}}) # 0/1 count+=res.nInserted; if(count%100000==0) print("inserted "+count+" time used:"+(((new Date()).getTime()-start.getTime())/1000)+" seconds"); } }catch(error){ print("Total doc inserted successfully:"+count); } }j:0不实时刷日志> journalDataLoss(0) Inserted 10000 times used: 3.579 seconds Inserted 20000 times used: 7.123 seconds ... ... <- execute: kill -9 mongod Total doc inserted successfully:715000 # 重启mongod,检查插入数量 > db.test.count() 713000 # 数据丢失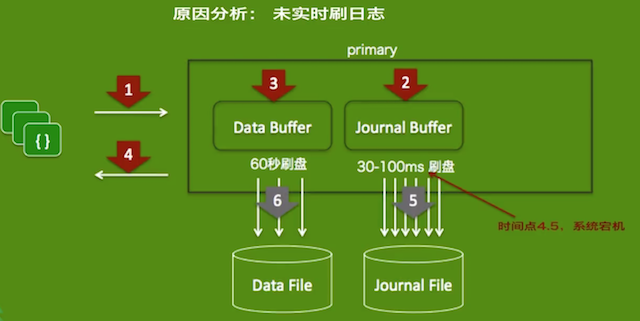
j:1实时刷日志> journalDataLoss(1) Inserted 10000 times used: 4.579 seconds Inserted 20000 times used: 8.123 seconds ... ... <- execute: kill -9 mongod Total doc inserted successfully:726000 # 重启mongod,检查插入数量 > db.test.count() 726000 # 数据未丢失
场景:主备置换导致数据丢失(eg:
w:1/majority,j:1高速持续写入数据,kill -9 mongod主节点,连接到新的主节点,检查实际插入的数据与程序汇报的插入数据)w:1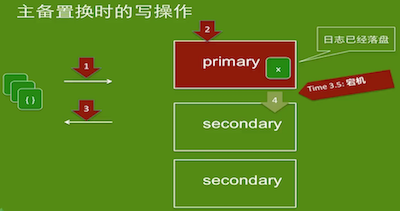
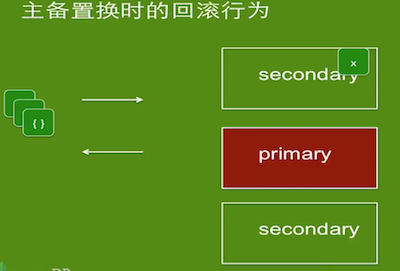
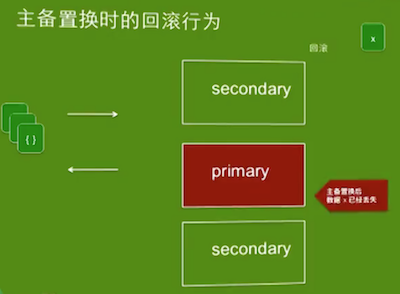
w:majority设置确认数据写到大部分节点再返回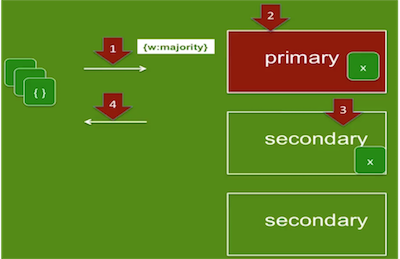
MongoDB数据安全总结


Read preference describes how MongoDB clients route read operations to the members of a replica set.By default, an application directs its read operations to the primary member in a replica set.
CRUD
Create(insert)
Insert Document into Collection 注:
- 单条document操作是原子性的
- 每一个document都有一个唯一的
_id字段作为 primary_key(若未指定,则MongoDB自动为_id生成一个ObjectId) _id字段值无法修改
db.myCollection.insert({...}) # 返回WriteResult对象
db.myCollection.insert([{},{},..]) # 返回BulkWriteResult对象
db.myCollection.insertOne({...})
db.myCollection.insertMany([{},{},..])
Read(find)
db.myCollection.find(<query filter>,<projection>)
db.myCollection.findOne(...)
// 参数<query filter>/<projection>格式:
{
<field1>: <value1>,
<field2>: { <operator>: <value> },
...
}
<query filter>- value:
- 普通特定值
{ <operator>: <value> }:specify conditions
operator:
# Comparison $eq,$gt,$gte,$lt,$lte,$ne,$in,$nin # Logical $or,$and,$not,$nor # Element $exists,$type # Evaluation $mod,$regex,$text,$where # Geospatial $geoWithin,$geoIntersects,$near,$nearsphere # Array $all,$elemMatch,$size # Bitwise $bitsAllSet,$bitsAnySet,$bitsAllClear,$bitsAnyClear # Comments $comment
- value:
<projection>- value:
1/true: 返回文档包含该字段0/false: 返回文档排除该字段{ <operator>: <value> }: specify conditions
- operator:
$,$elemMatch,$slice,$meta - 注:不能使用数组索引来指定映射的特定数组元素,eg:
{ "ratings.0": 1 } -- wrong
- value:
示例:
查询
db.users.find( { status:"A" } ) db.users.find( { status:{ $in:["P","D"] } } ) db.users.find({ status:"A", $or:[ {age:{$lt:30}},{type:1} ] }) # 嵌入式document匹配 db.users.find({ favorites:{artist:"Picasso"} }) db.users.find({ "favorites.artist":"Picasso" }) # 精确匹配 db.users.find({ badges:["blue","black"] }) # 匹配包含black的 db.users.find({ badges:"black" }) # 匹配第一个元素为black的 db.users.find({ "badges.0":"black" }) # 查询 finished 数组至少包含一个大于15并且小于20的元素的文档 # $elemMatch 为数组元素指定复合条件,查询数组中至少一个元素满足所有指定条件的文档 db.users.find({ finished: { $elemMatch: { $gt: 15, $lt: 20 } } }) # 查询 finished 数组中包含大于15 ,或者小于20的元素的文档 db.users.find({ finished: { $gt: 15, $lt: 20 } })查询返回部分字段
// 返回文档 _id,name,status 字段 db.users.find( {status:"A"}, {name:1,status:1} ) // 返回文档 name,status 字段 // Note: 除了 _id 字段,不能在映射文档中组合包含和排除语句 // Eg: name:1,status:0 -- wrong! db.users.find({ {status:"A"}, {name:1,status:1,_id:0} }) // 返回文档不显示 favorites,points字段 db.users.find({ {status:"A"}, {favorites:0,points:0} }) // 返回文档显示_id,name,status,points的bonus字段 db.users.find({ {status:"A"}, {name:1,status:1,"points.bonus":1} }) // 使用$slice映射操作符来返回 points数组中最后的元素 db.users.find({ {status:"A"}, {name:1,status:1,"points":{$slice:-1}} })
注:
查询值为Null或不存在的字段
{ "_id" : 900, "name" : null }, { "_id" : 901 }db.users.find({name:null}): 会返回name为null和不存在name字段的记录(注:若使用了sparse稀疏索引,只会匹配到name为null的记录,不会匹配到不存在的)db.users.find({name:{$type:"null"}}): 只会返回name为null的记录 ($type类型筛查)db.users.find({name:{$exists:false}}): 只返回不存在name字段的documents ($exists存在性筛查)
游标Cursor
var myCursor=db.users.find({type:"string"}) while(myCursor.hasNext()){ printjson(myCursor.next()) } myCursor.forEach(printjson); myCursor.forEach(function(myDoc){ print("user:"+myDoc.name); }) var myArray=myCursor.toArray(); myArray[3]; myCursor[1] // same with myCursor.toArray()[1]find方法返回的(若不赋给一个变量,则会自动遍历显示,默认是展示20条记录,可以使用DBQuery.shellBatchSize来改变迭代结果的数量)- Cursor Method: count,hint,forEach,map,limit,sort,size,skip,toArray,... More
Update
db.myCollection.update(<query filter>,<update document>,<option>) # 默认情况下只更新 一个 文档
db.myCollection.updateOne(...)
db.myCollection.updateMany(...)
db.myCollection.replaceOne(...)
// 更多:
db.myCollection.findOneAndReplace()
db.myCollection.findOneAndUpdate()
db.myCollection.findAndModify()
<query filter>: 同上<update document>:{ <field1>: <value1>, ... }{<update operator>: { <field1>: <value1>, ... },...}update operators:
# Field $inc $mul $rename $setOnInsert $set $unset $min $max $currentDate # Array $ $[] $[<identifier>] $addToSet $pop $pull $push $pullAll # Modifiers $each $position $slice $sort # Bitwise $bit
<option>- multi:false/true 配置是否更新多个文档
- upsert:false/true 表示不存在时是否插入新的document
示例:
db.users.update( { name: "xyz" }, { name: "mee", age: 25, type: 1, status: "A", favorites: { "artist": "Matisse", food: "mango" } } ) db.users.update( {status:"A"}, { $set:{status:"B",type:0}, $currentDate:{lastModified:true} }, {multi:true} )
Delete
// delete
db.myCollection.deleteOne(<query filter>)
// delete all matched
db.myCollection.deleteMany(...)
db.myCollection.remove(<query filter>, <justOne>)
// delete all,include index
db.myCollection.drop()
// 删除以指定顺序排序的文档中的第一个文档.
db.myCollection.findOneAndDelete().
示例:
// delete all documents
db.users.deleteMany({})
db.users.remove({})
// delete all matched
db.users.remove({status:"D"})
db.users.deleteMany({status:"D"})
// delete just one
// <justOne>:1
db.users.remove({status:"D"},1}
db.users.deleteOne({status:"D"})
WriteConcern
在安全写情况下,可以指定MongoDB写操作要求的确认级别(insert/update/delete 操作的最后一个参数)
{ w: <value>, j: <boolean>, wtimeout: <number> }
w:0/1/"majority" -- write acknowledgement instancej:true/false -- journalwtimeout-- only applicable for w>1
索引 Index
- 优点:加快索引相关的查询;
- 缺点:增加磁盘空间消耗,降低写入性能
CRUD
创建索引
// <field>: < 1 or -1 > // 1 : 索引正序,-1 : 索引倒序 db.collection.createIndex( <Key Index specification>, <options>)查看索引
db.collection.getIndexes()删除索引
db.collection.dropIndex({...}) db.collection.dropIndexs()重建索引: ( drop all indexes,include _id index,then rebuilds all in the background,rebuild _id index in the foreground,which takes the db's write lock.)
db.collection.reIndex()检查索引
// 扫描集合中的数据和索引以检查正确性的内部命令 db.collection.validate()
单字段/复合/多键索引
单字段索引 Single Field Index
db.users.createIndex({age:-1});- 在任意一个field上(包括Embedded Field)建立索引
- 默认索引
_id:类型ObjectId(代替递增的 id,能够解决分布式的 MongoDB 生成唯一标识符的问题),12个字节构成:Timestamp(4)+MachineIdentifier(3)+ProcessIdentifier(2)+Coounter(3) - 可配置顺序/倒序(
1: 正序,-1:倒序)
复合索引 Compound Index
db.users.createIndex( { username: 1, age: -1 } ) db.users.createIndex( { username: 1, age: 1 } ) // 方便按照username和age查找 db.users.find({username:"Tom",age:5});- 多个不同field组成
- 注:上面的两个索引是完全不同的,在磁盘上的
B+树其实也按照了完全不同的顺序进行存储,在使用查询语句对集合中数据进行查找时,是会使用不同的索引,所以在索引创建时要考虑好使用的场景,避免创建无用的索引。
多键索引 Multikey Index
//{ _id: 1, item: "ABC", ratings: [ 2, 5, 9 ] } db.survey.createIndex( { ratings: 1 } )- 在一个储存数组的键上添加索引,会对数组中的每个元素都添加索引项,加速对数组中元素的查找
- 注:不需要显示地指定索引为多键类型,MongoDB会自动地决定是否需要创建一个多键索引
文本索引
Text Index 文本索引(也叫全文索引)
- 支持在字符串内容上的文本检索查询
- 一个集合只能有一个文本检索索引,但是这个索引可以覆盖多个字段
- 创建文本索引(
name:"text"):db.stores.createIndex({name:"text",description:"text"}) # 在name,description字段建立文本索引 - 查询:使用
$text操作符在一个创建了text index的Collection上执行文本检索{ $text: { $search: <string>, $language: <string>, $caseSensitive: <boolean>, $diacriticSensitive: <boolean> } } - 查询示例:
$text会使用空格和标点符号作为分隔符对检索字符串进行分词 (OR操作)// 包含 aa or bb or cc db.stores.find({ $text:{$search:"aa bb cc"} }) // 包含 (aa or bb ) and not cc db.stores.find({ $text:{$search:"aa bb -cc"} }) // 包含 aa or "bb cc" db.stores.find({ $text:{$search:"aa \"bb cc\""} })$text+$meta显示匹配相似度# Sort by Additional Query and Text Search Score and Return top 2 matching documents # score: 计算一个相关性分数,表明该文档与查询的匹配程度 # 显式地对 $meta:"textScore" 字段进行映射然后基于该字段进行sort排序 db.stores.find({ {$text:{$search:"aa bb cc"}}, {score:{$meta:"textScore"}} }).sort({ date:1, score:{$meta:"textScore"} }).limit(2)- 聚合管道中,在 $match 阶段使用文本搜索(限制:只能是管道中的第一个阶段,$text只能在阶段中出现一次,$text不能出现在$or,$nor表达式中)
db.articles.aggregate([ { $match:{ $text:{$search:"aa bb"} } }, { $sort:{ score:{$meta:"textScore"} } }, { $project:{ title:1,_id:0 } } ]) db.articles.aggregate([ { $match:{ $text:{$search:"aa bb"} } }, { $project:{ title:1,_id:0,score:{$meta:"textScore"} } }, { $match:{ score:{$gt:1.0} } } ])
- 注:如果要做更细致的全文索引的话,推荐使用 Elasticsearch
索引属性
创建索引时的可配置选项<options>,说明Index的一些特性
db.collection.createIndex( <Key Index specification>, <options>)
expireAfterSeconds(TTL): 过一段时间后自动移除集合中的documentdb.users.createIndex( {lastModifiedDate:1}, {expireAfterSeconds:3600} ) // 设置文档过期的时间expireAt字段的值一致 db.log_events.createIndex( { "expireAt": 1 }, { expireAfterSeconds: 0 } )- index 字段存储数据类型必需是date或date数组(若是数组,则其中最低过期阈值得到匹配时,删除此document)
- 不能保证过期数据会被立刻删除,删除过期数据的后台任务每隔60秒运行一次
- 应用场景:机器生成的事件数据,日志,会话信息等,这些数据都只需要在数据库中保存有限时间
uniquedb.members.createIndex( { "user_id": 1 }, { unique: true } )collation: Case Insensitive Indexesdb.fruit.createIndex( { type: 1}, { collation: { locale: 'en', strength: 2 } } )sparse( 稀疏索引): null值不计入索引,常和唯一索引连用db.users.createIndex({name:1},{sparse:true})partialFilterExpression( 局部索引Partial Indexes ):稀疏索引进化版,一种在指定赛道上(可跨赛道),消耗更低的索引db.users.createIndex( {name:1}, {unique:true,partialFilterExpression:{age:{$gt:18}}} )- 不能作为分片的片键
_id不能创建局部索引- 同一个索引不能和sparse同时使用
- 一个键上不能有多个不同的局部索引
- particalFilterExpression 支持的过滤操作:
$eq,$gt,$gte,$lt,$lte, $exists:true, $type, $and -- at top level
background: 后台创建索引会比默认的慢,但不会锁表(生产环境使用background:true比较好)db.users.createIndex({username:1},{background:true})
衡量索引使用情况
- mongostat工具-查看mongodb运行状态的程序
mongostat --help mongostat -h localhost:12345 - profile集合
db.getProfilingLevel() db.getProfilingStatus() db.setProfilingLevel(2) show tables db.system.profile.find().sort({$natural:-1}).limit(10) 日志
# 配置日志 vim conf/mongod.conf ... verbose = vvvvv # v,vv,...,vvvvv查看容量占用(注意: 确保索引与内存相适应)
// indexSizes: 查看索引在磁盘存储的大小 db.users.stats().indexSizes` // indexDetails: 查看索引占用内存的大小 (内存中会放最近使用的索引) db.users.stats({indexDetails:true}).indexDetails // totalIndexSize 查询索引大小 db.users.totalIndexSize()$indexStats索引具体信息// { $indexStats: { } } 返回包括 name,key,host,accesses字段 db.orders.aggregate([ { $indexStats: { } } ]) db.orders.aggregate([ { $indexStats: { } } , {$match:{name:"_id_ type_1_item_1"}} ]) // Eg: Return { "name" : "_id_", "key" : {"_id" : 1}, "host" : "examplehost.local:27017", "accesses" : { "ops" : NumberLong(0), "since" : ISODate("2015-10-02T14:31:32.479Z") } } { "name" : "type_1_item_1", "key" : {"type" : 1,"item" : 1}, "host" : "examplehost.local:27017", "accesses" : { "ops" : NumberLong(1), "since" : ISODate("2015-10-02T14:31:58.321Z") } }explain()返回查询计划(query plan),即查询的详细信息// 返回一个含有查询过程的统计数据的文档,包括所使用的索引,扫描过的文档数,查询所消耗的毫秒数 db.users.find(...).explain("executionStats")hint()以索引作为方法参数, 强制 MongoDB使用指定的索引来匹配查询db.people.find( { name: "John Doe", zipcode: { $gt: "63000" } } ).hint( { zipcode: 1 } ).explain("executionStats") // 指定 $natural 操作符来避免MongoDB使用任何索引(注; 亦即,查询不会使用索引) db.people.find( { name: "John Doe", zipcode: { $gt: "63000" } } ).hint( { $natural: 1 } ).explain("executionStats")
索引优化
索引策略:
- 创建索引以支持查询
- 使用索引来排序查询结果
- 确保索引与内存相适应
- 创建能确保选择力的查询
优化策略:
- 重复率越低越适合做索引(distinct/count 越接近1越适合),例如状态,性别等重复率不适合
- 联合索引,索引前缀由低到高,eg:
db.test.createIndex({a:1,b:1,c:1}),则 a b c, a b, a - 索引顺序:等值,范围,顺序
// 查询 db.test.find({ a:2, b:{$gt2,$le:10} }).sort({c:1}) // 则建立索引如下所以更优: db.test.createIndex({a:1,c:1:b:1}) - 有条件尽量匹配覆盖索引
db.test.createIndex({a:1,b:1,c:1}) db.test.find({a:3},{b:1,c:1,_id:0}) # select b,c from test where a=3 -> 能用到索引,且获取的值在索引中 - 指定
从节点创建索引,这样不影响主节点的写入,不会驱逐掉常规缓存(适用于BI,报表查询,需添加大量索引的情况),步骤:- 指定从节点priority为0 (不会变成主节点)
- 单机模式重启该从节点(配置文件注释)
- 添加索引
- 副本集模式重启该节点(配置文件还原)
聚合 Aggregate
MongoDB中有三种实现聚合的方式:
- 聚合管道 Aggregator pipeline
- Map-Reduce function
- 单目聚合方法(group,count,distinct)
聚合管道
Aggregation Pipeline
- 基于数据处理的聚合管道,使用内置的原生sql操作,效率高 (支持类似mysql的group by功能 )
- 每个document通过一个由多个阶段(stage)组成的管道,经过一系列的处理(例如对每个阶段的管道进行分组、过滤等)输出相应的结果
- 限制:
- 每个阶段管道限制为
100MB的内存,超过将报错(可以设置allowDiskUse为true来在聚合管道节点把数据写入临时文件来解决100MB的内存的限制) - 输出的结果只能保存在一个文档中,BSON Document大小限制为
16M(2.6后:DB.collect.aggregate()方法返回一个指针cursor ,可以返回任何结果集的大小) - 可作用在分片集合,但结果不能输在分片集合(MapReduce可作用在分片集合,结果也可输在分片集合)
- 每个阶段管道限制为
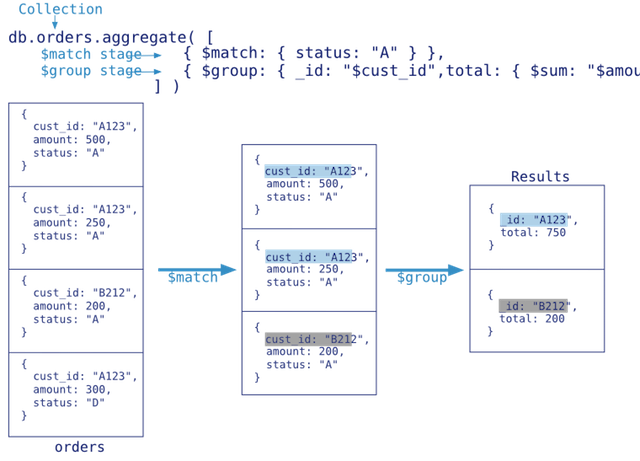
// 方式一:
db.collection.aggregate(pipeline, options)
// 方式二:
db.runCommand({
aggregate: "<collection>" || 1,
pipeline: [ <stage>, <...> ],
//options ( belows are optional )
explain: <boolean>,
allowDiskUse: <boolean>,
cursor: <document>,
maxTimeMS: <int>,
bypassDocumentValidation: <boolean>,
readConcern: <document>,
collation: <document>,
hint: <string or document>,
comment: <string>,
writeConcern: <document>
})
参数
pipeline:[<stage>,<Stage>,...] //<stage> $stageOperator:{<key>:<value>,<key>:<expression>...} // <expression> { <expressionOperator>:<arg> } { <expressionOperator>:[<arg1>,<arg2>,... <argN>] }StageOperator 阶段操作符
$match // 过滤数据,传输到下一个阶段管道 $project // 投影,过滤显示文档字段(可选择字段,重命名字段,派生字段) $group // 将数据根据key进行分组,统计结果 $unwind // 将文档中的某一个数组类型字段拆分成多条,每条包含数组中的一个值 $lookup // 进行两个集合之间左连接操作 $sort // 将输入文档排序后输出 $skip // 跳过指定数量的文档,返回余下的文档 $limit // 限制返回的文档数 $redact // 根据字段所处的document结构的级别,对文档进行“修剪”,通常和“判断语句if-else”结合使用,即$cond $sample // 抽样输出 $geoNear // 用于地理位置数据分析 $indexStats // 返回数据集合的每个索引的使用情况 { $indexStats: { } } $out // 将最后计算结果写入到指定的collection中,必须为pipeline最后一个阶段管道 ... // 常用组合 $match -> $project $match -> $group $match -> $group -> $sort $match -> $match -> $ project -> $group $match -> $lookup -> $match -> $sort $match -> $project -> $sort -> $skip -> $limit $match -> $project -> $unwind -> $group -> $sort ->$skip -> $limitExpressionOperator 表达式操作符
// 1. 布尔管道 Boolean Operators // eg: $or: [ { $gt: [ "$qty", 250 ] }, { $lt: [ "$qty", 200 ] } ] $and,$or,$not // 2. 条件操作符 Conditinal Operator // eg: $cond: { if: { $gte: [ "$qty", 250 ] }, then: 30, else: 20 } $cond,$ifNull,$switch // 3. 数据类型 DataType Operators $type // 4. 集合操作 Set Operators // eg: $setUnion: [ "$A", "$B" ] $setEquals // 完全相等 $setIsSubset // 完全被包含 $anyElementTrue // 集合中任一元素符合,则true $allElementsTrue // 集合中所有元素符合,则true $setIntersection // 交集 $setUnion // 并集 $setDifference // 差集 // 5. 比较操作符 Comparison Operators $cmp // 0/1/-1 $eq,$gt,$lt,$gte,$lte,$ne // 6. 算术操作符 Arithmetic Operators // eg: $abs: { $subtract: [ "$start", "$end" ] } $abs // 绝对值 $in $add, $substract, $multiply, $divide, $mod $ceil, $floor ,$trunc $log, $log10, $sqrt, $pow, $exp // 7. 字符串操作 String Operators // eg: $split: ["$city", ", "] $concat, $split $trim, $ltrim, $rtrim $toLower, $toUpper $toString $dateFromString, $dateToString $strcasecmp // case-insensitive,return 0,1/-1 $substr // Deprecated! $substrBytes, $substrCP $indexOfBytes, $indexOfCP $strLenBytes,$strLenCP // 8. 数组 Array Operators // eg: $arrayElemAt: [ "$favorites", -1 ] $arrayElemAt $map $filter $slice // subset $zip // merge two arrays $reduce // combine into a single value return $isArray, $arrayToObject, $objectToArray $concatArrays $reverseArray $indexOfArray $in $range $size // 9. 日期 Date Operators $dateFromParts, $dateToParts $dateFromString, $dateToString $dateOfMonth, $dateOfWeek, $dateOfYear $year,$month, $week, $hour, $minute, $second, $millisecond $isoDayOfWeek, $isoWeek, $isoWeekYear $toDate ...
参数
options:{ explain: <boolean>, allowDiskUse: <boolean>, cursor: <document>, maxTimeMS: <int>, bypassDocumentValidation: <boolean>, readConcern: <document>, collation: <document>, hint: <string or document>, comment: <string>, writeConcern: <document> }
示例:
Prepare Test data
// catalogues: name,description db.catalogues.insert([ {name:"Spring",description:"spring framework"}, {name:"ReactJS",description:"reactJS front framework"}, {name:"NoSql",description:"not only sql databases"} {name:"Docker",description:"Build, Ship, and Run Any App, Anywhere"} ]); // articles: title,author,description,tags,catalogue,postDate,content db.articles.insert([ {title:"Spring Basic",author:"Tom",description:"introduce spring basic",tags:["java","spring"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"Spring"})._id,postDate:"2015-01-01",content:"spring basic:ioc,aop",click:1}, {title:"Spring MVC",author:"Tom",description:"introduce spring mvc",tags:["java","spring","mvc"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"Spring"})._id,postDate:"2015-01-11",content:"spring mvc:dispatchServlet,restful",click:5}, {title:"Spring Security",author:"Tom",description:"introduce spring security",tags:["java","spring","security"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"Spring"})._id,postDate:"2015-01-21",content:"spring security:securityFilter,authentication,accessDecide",click:20}, {title:"ReactJS Basic",author:"Lucy",description:"introduce reactJS front framework basic",tags:["front","reateJS"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"ReactJS"})._id,postDate:"2015-02-01",content:"reactJS basic:component,lifecycle,props,state",click:30}, {title:"ReactJS Flux",author:"Lucy",description:"introduce reactJS Flux",tags:["front","reateJS"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"ReactJS"})._id,postDate:"2015-02-11",content:"reactJS Flux:reflux,redux"}, {title:"Redis",author:"Jack",description:"introduce redis key-value db",tags:["nosql","redis"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"NoSql"})._id,postDate:"2015-03-11",content:"redis:install,master-slave,persist,subscribe,crud",click:0}, {title:"MongoDB",author:"Jack",description:"introduce mongo document database",tags:["nosql","mongodb"],catalogueId:db.catalogues.findOne({name:"NoSql"})._id,postDate:"2015-03-21",content:"mongodb:mongo shell,crud,index,aggregation,replica,sharding",click:25} ]);$lookup: Join# $lookup # { # $lookup: { # from: <collection to join>, # localField: <field from the input documents>, # foreignField: <field from the documents of the "from" collection>, # as: <output array field> # } # } > db.catalogues.aggregate([ {$project:{id:1,name:1}}, { $lookup:{ from:"articles", localField:"_id", foreignField:"catalogueId" ,as:"articles"} }, {$project:{"_id":0,"name":1,"articles.title":1,"articles.click":1}} ]) { "name" : "Spring", "articles" : [ { "title" : "Spring Basic", "click" : 1 }, { "title" : "Spring MVC", "click" : 5 }, { "title" : "Spring Security", "click" : 20 } ] } { "name" : "ReactJS", "articles" : [ { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "click" : 30 }, { "title" : "ReactJS Flux" } ] } { "name" : "NoSql", "articles" : [ { "title" : "Redis", "click" : 0 }, { "title" : "MongoDB", "click" : 25 } ] } { "name" : "Docker", "articles" : [ ] }$group: 按照特定的字段的值进行分组(非流式运算:必须等收到所有的文档之后,才能对文档进行处理)> db.articles.count() 7 # 1. $sum # select count(*) as count from articles; > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"null",count:{$sum:1}} } ]) { "_id" : "null", "count" : 7 } # select catalogueId as _id,count(*) as count as from articles group by catalogueId > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$catalogueId",count:{$sum:1}} } ]) { "_id" : ObjectId("5b8e342212b995b45c17d5ec"), "count" : 2 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5b8e342212b995b45c17d5eb"), "count" : 2 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5b8e342212b995b45c17d5ea"), "count" : 3 } # select author as _id, sum(click) as total_click from articles group by author > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",total_click:{$sum:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "total_click" : 30 } { "_id" : "Jack", "total_click" : 25 } { "_id" : "Tom", "total_click" : 26 } # 2. $max/$min # select author as _id, max(click) as max_click from articles group by author > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",max_click:{$max:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "max_click" : 30 } { "_id" : "Jack", "max_click" : 25 } { "_id" : "Tom", "max_click" : 20 } # 3. $avg # select author as _id, avg(click) as avg_click from articles group by author > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",avg_click:{$avg:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "avg_click" : 30 } { "_id" : "Jack", "avg_click" : 12.5 } { "_id" : "Tom", "avg_click" : 8.666666666666666 } # 4. $first/$last > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",click_list:{$first:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "click_list" : 30 } { "_id" : "Jack", "click_list" : 0 } { "_id" : "Tom", "click_list" : 1 } # 5. $push/$addToSet > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",click_list:{$push:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "click_list" : [ 30 ] } { "_id" : "Jack", "click_list" : [ 0, 25 ] } { "_id" : "Tom", "click_list" : [ 1, 5, 20 ] }$match过滤(尽量放在前面,提高效率)# select _id,title,author from articles where click>0 and click<25 db.articles.aggregate([ { $match:{click:{$gt:0,$lt:25}} }, { $project:{"_id":0,"title":1,"author":1,"click":1}} ]) { "title" : "Spring Basic", "author" : "Tom", "click" : 1 } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "author" : "Tom", "click" : 5 } { "title" : "Spring Security", "author" : "Tom", "click" : 20 } # select author as _id,sum(click) as total_click from articles group by author having sum(click)>0 and sum(click)<30 db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",total_click:{$sum:"$click"} } }, { $match:{total_click:{$gt:0,$lt:30}} } ]) { "_id" : "Jack", "total_click" : 25 } { "_id" : "Tom", "total_click" : 26 }$project: 选择字段,重命名字段,派生字段# 选择字段: field:1/0,表示选择/不选择 field;将无用的字段从pipeline中过滤掉,能够减少聚合操作对内存的消耗 > db.articles.aggregate([ { $project:{"_id":0,"title":1,"postData":1,"click":1,"tags":1} } ]) { "title" : "Spring Basic", "tags" : [ "java", "spring" ], "click" : 1 } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "tags" : [ "java", "spring", "mvc" ], "click" : 5 } { "title" : "Spring Security", "tags" : [ "java", "spring", "security" ], "click" : 20 } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "tags" : [ "front", "reateJS" ], "click" : 30 } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "tags" : [ "front", "reateJS" ] } { "title" : "Redis", "tags" : [ "nosql", "redis" ], "click" : 0 } { "title" : "MongoDB", "tags" : [ "nosql", "mongodb" ], "click" : 25 } # 重命名字段: 引用符$,格式是:"$field",表示引用doc中 field 的值 > db.articles.aggregate([ { $project:{_id:0,title:1,"preClick":"$click"} } ]) { "title" : "Spring Basic", "preClick" : 1 } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "preClick" : 5 } { "title" : "Spring Security", "preClick" : 20 } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "preClick" : 30 } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux" } { "title" : "Redis", "preClick" : 0 } { "title" : "MongoDB", "preClick" : 25 } # 派生字段: 对字段进行计算,派生出一个新的字段 > db.articles.aggregate([ { $project:{ "title":1, "click":1, "result": { $or: [ { $gt: [ "$click", 20 ] }, { $lt: [ "$click", 100 ] } ] } } } ]) { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b54816"), "title" : "Spring Basic", "click" : 1, "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b54817"), "title" : "Spring MVC", "click" : 5, "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b54818"), "title" : "Spring Security", "click" : 20, "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b54819"), "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "click" : 30, "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b5481a"), "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b5481b"), "title" : "Redis", "click" : 0, "result" : true } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be2b3347ec0ecb208b5481c"), "title" : "MongoDB", "click" : 25, "result" : true } # 派生字段 > db.articles.aggregate([ { $project:{ _id:0, title:1, click:1, level: { $cond:{if:{$gte:["$click",20]},then: "High",else: "Low"} } } } ]) { "title" : "Spring Basic", "click" : 1, "level" : "Low" } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "click" : 5, "level" : "Low" } { "title" : "Spring Security", "click" : 20, "level" : "High" } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "click" : 30, "level" : "High" } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "level" : "Low" } { "title" : "Redis", "click" : 0, "level" : "Low" } { "title" : "MongoDB", "click" : 25, "level" : "High" }$limit,$skip,$sort> db.articles.aggregate([ {$skip:2}, {$limit:3}, {$sort:{"postDate":1}}, {$project:{"_id":0,"title":1,"postDate":1}} ]) { "title" : "Spring Security", "postDate" : "2015-01-21" } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "postDate" : "2015-02-01" } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "postDate" : "2015-02-11" } > db.articles.aggregate([ {$sort:{"postDate":1}}, {$limit:3}, {$skip:2}, {$project:{"_id":0,"title":1,"postDate":1}} ]) { "title" : "Spring Security", "postDate" : "2015-01-21" }$unwind: 拆分数组字段> db.articles.aggregate([ {$project:{"_id":0,"title":1,"tags":1}}, {$unwind:"$tags"} ]) { "title" : "Spring Basic", "tags" : "java" } { "title" : "Spring Basic", "tags" : "spring" } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "tags" : "java" } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "tags" : "spring" } { "title" : "Spring MVC", "tags" : "mvc" } { "title" : "Spring Security", "tags" : "java" } { "title" : "Spring Security", "tags" : "spring" } { "title" : "Spring Security", "tags" : "security" } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "tags" : "front" } { "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "tags" : "reateJS" } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "tags" : "front" } { "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "tags" : "reateJS" } { "title" : "Redis", "tags" : "nosql" } { "title" : "Redis", "tags" : "redis" } { "title" : "MongoDB", "tags" : "nosql" } { "title" : "MongoDB", "tags" : "mongodb" }- 参数数组字段为空或不存在时,待处理的文档将会被忽略,该文档将不会有任何输出
- 参数不是一个数组类型时,将会抛出异常
$out: 把执行的结果写入指定数据表(会先清空原数据)> db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",total_click:{$sum:"$click"}} }, { $out:"author_click" } ]) > db.author_click.find() { "_id" : "Lucy", "total_click" : 30 } { "_id" : "Jack", "total_click" : 25 } { "_id" : "Tom", "total_click" : 26 } > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",total_click:{$sum:"$click"}} }, { $project:{"_id":0}}, { $limit:2}, { $out:"author_click" } ]) > db.author_click.find() { "_id" : ObjectId("5be3a0ec58072db74ca83569"), "total_click" : 30 } { "_id" : ObjectId("5be3a0ec58072db74ca8356a"), "total_click" : 25 }options:
explain返回aggregate各个阶段管道的执行计划信息> db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",click_list:{$push:"$click"}} } ]) { "_id" : "Lucy", "click_list" : [ 30 ] } { "_id" : "Jack", "click_list" : [ 0, 25 ] } { "_id" : "Tom", "click_list" : [ 1, 5, 20 ] } > db.articles.aggregate([ { $group:{_id:"$author",click_list:{$push:"$click"}} } ],{explain:true}) { "stages" : [ { "$cursor" : { "query" : { }, "fields" : { "author" : 1, "click" : 1, "_id" : 0 }, "queryPlanner" : { "plannerVersion" : 1, "namespace" : "demo.articles", "indexFilterSet" : false, "parsedQuery" : { }, "winningPlan" : { "stage" : "COLLSCAN", "direction" : "forward" }, "rejectedPlans" : [ ] } } }, { "$group" : { "_id" : "$author", "click_list" : { "$push" : "$click" } } } ], "ok" : 1 }
Map-Reduce
- 是一种计算模型(能够在多台Server上并行执行),将大批量的工作(数据)分解(MAP)执行,然后再将结果合并成最终结果(REDUCE)
- 分为两个阶段:Map和Reduce;主要分为三步:Map,Shuffle,Reduce
- Map: 将操作映射到每条document,产生key和value。eg:Map一个document产生key value对:
{female,{count:1}},{male,{count:1}} - Shuffle: 按照key进行分组,并将key相同的value组合成数组。eg:产生
(female:[{count:1},{count:1},...]),(male:[{count:1},{count:1},...]) - Reduce: 把Value数组化简为单值(聚合运算统计)。eg:
(female:{count:20}),(male:{count:15}) - 注:Map和Reduce需要显式定义,shuffle由MongoDB来实现
- Map: 将操作映射到每条document,产生key和value。eg:Map一个document产生key value对:
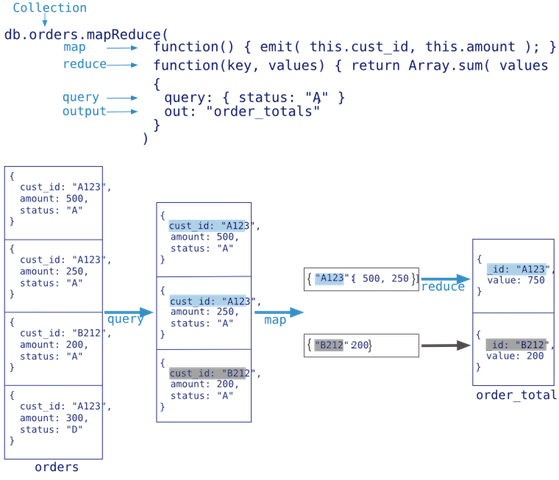
db.collection.mapReduce(
<map>, // map 映射函数,生成键值对 (遍历 collection,调用emit(key, value))
<reduce>, // reduce 统计函数 (key-values -> key-value,把values数组变成一个单一的值value)
{
out: <collection>, // 存放统计结果 (不指定则使用临时集合,在客户端断开后自动删除)
query: <document>, // 一个筛选条件,只有满足条件的文档才会调用map函数
sort: <document>, // 发往map函数前给文档排序
limit: <number>, // 发往map函数的文档数量的上限
finalize: <function>,
scope: <document>,
jsMode: <boolean>,
verbose: <boolean>,
bypassDocumentValidation: <boolean>
}
)
示例:
> db.articles.find({},{"_id":0,"title":1,"author":1,"click":1,"tags":1})
{ "title" : "Spring Basic", "author" : "Tom", "tags" : [ "java", "spring" ], "click" : 1 }
{ "title" : "Spring MVC", "author" : "Tom", "tags" : [ "java", "spring", "mvc" ], "click" : 5 }
{ "title" : "Spring Security", "author" : "Tom", "tags" : [ "java", "spring", "security" ], "click" : 20 }
{ "title" : "ReactJS Basic", "author" : "Lucy", "tags" : [ "front", "reateJS" ], "click" : 30 }
{ "title" : "ReactJS Flux", "author" : "Lucy", "tags" : [ "front", "reateJS" ] }
{ "title" : "Redis", "author" : "Jack", "tags" : [ "nosql", "redis" ], "click" : 0 }
{ "title" : "MongoDB", "author" : "Jack", "tags" : [ "nosql", "mongodb" ], "click" : 25 }
# 1. 各author的click大于0的文章总数
> db.articles.mapReduce(
function(){emit(this.author,1)},
function(key,values){return Array.sum(values)},
{query:{click:{$gt:0}},out: "author_sum"}
)
{
"result" : "author_sum", // 储存结果的collection的名字
"timeMillis" : 122, // 执行花费的时间,毫秒为单位
"counts" : {
"input" : 5, // 满足条件被发送到map函数的文档个数
"emit" : 5, // 在map函数中emit被调用的次数,也就是所有集合中的数据总量
"reduce" : 1, // reduce函数调用次数
"output" : 3 // 结果集合中的文档个数
},
"ok" : 1 // 是否成功,成功为1
}
> db.author_sum.find()
{ "_id" : "Jack", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "Lucy", "value" : 1 }
{ "_id" : "Tom", "value" : 3 }
# 2. 各author文章的平均点击数
> db.articles.mapReduce(
function(){emit(this.author,{click:this.click||0,article:1})},
function(key,values){
reducedVal={sum_click:0,sum_article:0};
values.forEach(function(item){
reducedVal.sum_click+=item.click;
reducedVal.sum_article+=item.article;
})
return reducedVal.sum_click/reducedVal.sum_article;
},
{out:"author_sum"}
)
{
"result" : "author_sum",
"timeMillis" : 241,
"counts" : {
"input" : 7,
"emit" : 7,
"reduce" : 3,
"output" : 3
},
"ok" : 1
}
> db.author_sum.find()
{ "_id" : "Jack", "value" : 12.5 }
{ "_id" : "Lucy", "value" : 15 }
{ "_id" : "Tom", "value" : 8.666666666666666 }
单目聚合操作
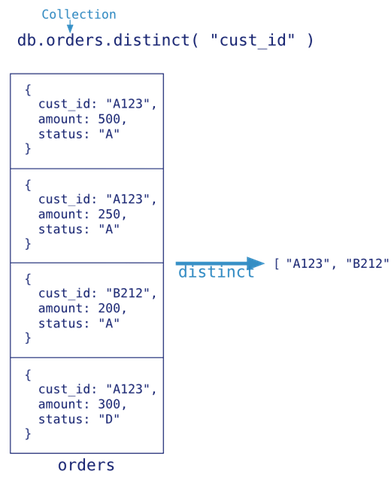
count:
db.collection.count(query, options)> db.articles.count() 7 > db.articles.count({click:{$gt:10}}) 3 > db.articles.count({click:{$gt:10},tags:{$size:2}}) 2 > db.articles.find({click:{$gt:10},tags:{$size:2}}).count() 2distinct:
db.collection.distinct(field, query, options)> db.articles.distinct("click") [ 1, 5, 20, 30, 0, 25 ] > db.articles.distinct("tags") ["java","spring","mvc","security","front","reateJS","nosql","redis","mongodb"] > db.articles.distinct("tags",{click:{$gt:20}}) [ "front", "reateJS", "mongodb", "nosql" ]
Security
安全:
- 物理隔离(最安全)
- 网络隔离
- IP白名单隔离(防火墙配置等)
- 用户名密码鉴权
开启权限认证:
- auth开启
> vim conf/mongod.conf ... auth = true - keyfile开启
操作:
查看用户
db.getUsers(),查看角色db.getRoles()> use admin switched to db admin > db.getUsers() [ { "_id" : "admin.mongoadmin", "user" : "mongoadmin", "db" : "admin", "roles" : [ { "role" : "root", "db" : "admin" } ], "mechanisms" : [ "SCRAM-SHA-1", "SCRAM-SHA-256" ] } ] > db.getRoles() [ ]创建用户
db.createUser(role内建类型:read,readWrite,dbAdmin,dbOwner,userAdmin)> db.createUser({ user:"cj", pwd:"123", roles:[ {role:"userAdmin",db:"demo"}, {role:"read",db:"local"} ] }) > mongo localhost:12345 -u cj -p 123 > use testdb > show tables创建角色
db.createRole# 用户角色: # 数据库角色(read,readWrite,dbAdmin,dbOwner,userAdmin) # 集群角色(clusterAdmin,clusterManager,...) # 备份角色(backup,restore,...) # 其他特殊权限(DBAdminAnyDatabase,...) > db.createRole({ role:"appUser", db:"myApp" privileges:[ { resource:{db:"myApp",collection:" "}, actions:["find","createCollection","dbStates","collStats"] }, { resource:{db:"myApp",collection:"logs"}, actions:["insert"] }, { resource:{db:"myApp",collection:"data"}, actions:["insert","update","remove","compact"] }, { resource:{db:"myApp",collection:"system.indexes"}, actions:["find"] } ], roles:[] })
复制集 & 分片
- 复制集 Replica Set (纵向): 基于领导(Leader-based)复制状态机 (关键:选举和数据复制)
- 分片 Sharding(横向):将数据进行拆分,水平的分散到不同的服务器上;架构上:读写均衡,去中心化
- 分片与复制集集群对比
- Shard Replication 实现意义|提升并发性能,提高大量数据随机访问性能|数据冗余,提升读性能 架构上|水平化|中心化 实现原理|数据打散分布|数据镜像 维护成本|相对较高|相对容易
More about Sharding
分片成员节点:
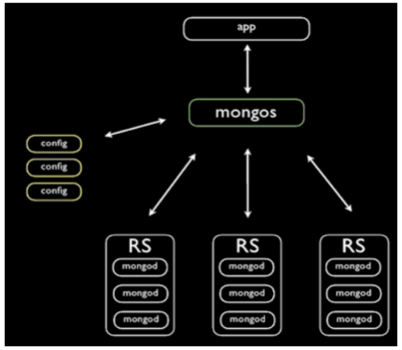
Shard节点: 存储数据的节点(单个mongod或者副本集)mongod --shardsvr --rpelSetConfig Server:存储元数据,为mongos服务,将数据路由到Shardmongod --configsvrQuery routers: 查询路由节点,即Mongos节点,接入Client请求,根据路由规则转发给合适的shard或者shardsmongos --configdb <configdb server>
概念:
- 分片片键(Shard Key):集合里面选个键,用该键的值作为数据拆分的依据,例如配置
sh.shardCollection("records.people", {user_id:"hashed"}) - 数据块(Chunk):mongodb分片后,存储数据的单元块,默认大小为64M
- 拆分 (Split Chunk):一个后台进程避免chunk增长的过大,当chunk尺寸超过指定的chunk size时,拆分此chunk(split后shard将会修改config server上这个chunk的metadata元信息)
- 平衡 (Balancing Chunks):一个后台线程用于对chunks迁移以达到平衡,会周期性的检查分片是否存在不均衡,如果存在则会进行块的迁移(balancer均衡器运行在mongos上,注:balancer进行均衡的条件是块数量的多少,而不是块大小)
- 拆分->平衡过程:
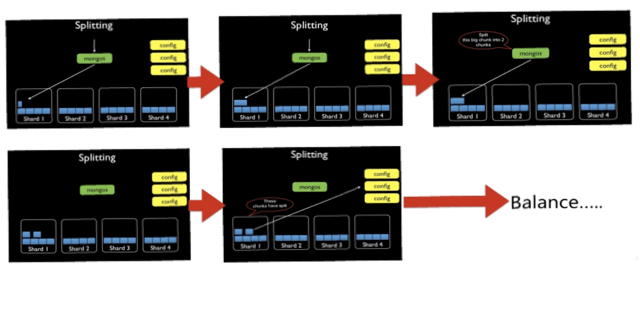
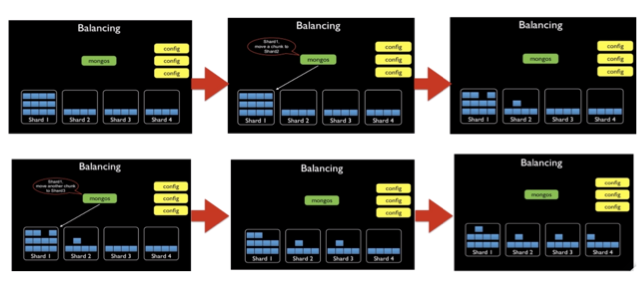
- 分片片键(Shard Key):集合里面选个键,用该键的值作为数据拆分的依据,例如配置
Sharding Strategy:
- Hashed Sharding(哈希切片) : 能将写入均衡分布到各个 shard
- Ranged Sharding(范围切片): 能很好的支持基于 shard key的范围查询
- Tag aware Sharding
- 好的shard key:
- key分布足够离散 sufficient cardinality: 片键相同导致数据块不拆分,容易形成大的数据块,导致数据不均
- 写请求均匀分布 (evenly distributed write): 例如单调递增的
_id或者时间戳作为片键,会导致一直往最后一个复本集添加数据 - 尽量避免 scatter-gather 查询 (targeted read)
添加分片过程:
- 连接到mongos
- Add Shards
- Enable Sharding
- 对一个Collection进行分片
示例:手动分片(减少自动平衡过程带来的IO等资源消耗,前提:充分了解数据,对数据进行预先划分)
# 关闭自动平衡 auto balance sh.stopBalancer() # Currently enabled: no # 分片切割 spliting > use admin > db.runCommand({"enablesharding":"myapp"}) > db.runCommand({"shardcollection":"myapp.users","key":{"email":1}}) for(var x=97;x<97+26;x++){ for(var y=97;y<97+26;y+=6){ var prefix=String.fromCharCode(x)+String.fromCharCode(y); db.runCommand({split:"myapp.users",middle:{email:prefix}}) } } # 手动移动分割块 balancing var shServer=[ "ShardServer 1", "ShardServer 2", "ShardServer 3", "ShardServer 4", "ShardServer 5" ] for(var x=97;x<97+26;x++){ for(var y=97;y<97+26;y+=6){ var prefix=String.fromCharCode(x)+String.fromCharCode(y); db.adminCommand({moveChunk:"myapp.users",find:{email:prefix},to:shServer[(y-97)/6]}) } } # 循环(y-97)/6的数值结果为0,6,12,18,24; shServer[0] -> shServer[4]
MongoDB 4.0 新特性
多文档事务
- 4.0: 单文档事务 -> 跨文档事务
- 4.2: 复制集事务 -> 分片集群事务
聚合类型转换: 引入
$convert聚合操作符来简化ETL(抽取,转化,加载)流程和负荷- 可结合:
# 1. 类型转换 $toBool,$toDate,$toDecimal,$toDouble,$toInt,$toLong,$toObjectId,$toString # 2. 日期操作转换 $dateToParts,$dateFromParts,$dateFromString # 3. 修剪 $trim,$rtrim,$ltrim {$trim:{input:<expression>}} {$trim:{input:[<expression>],chars:<string>}} - prepare test data:
> db.address.insert([ { street: "Canal st", building: NumberDecimal(21), _id: 0}, { street: "43rd st", building: "229", _id: 1}, { street: "Fulton st", building: "31", _id: 2 }, { street: "52nd st", building: "11w", _id: 3}, { street: "78th st", building: null, _id: 4}, { street: "78th st", _id: 5}, { street: "Rector st", building: NumberInt(10), _id: 6,last_visited: {year: 2017, month: 10}} ]); $convert示例:> db.address.aggregate( [ { $addFields: { building: { $convert: { input: "$building", to: "int", onError: 0, onNull: -1 } } } }, { $sort: {building: 1}} ]); { "_id" : 4, "street" : "78th st", "building" : -1 } { "_id" : 5, "street" : "78th st", "building" : -1 } { "_id" : 3, "street" : "52nd st", "building" : 0 } { "_id" : 6, "street" : "Rector st", "building" : 10, "last_visited" : { "year" : 2017, "month" : 10 } } { "_id" : 0, "street" : "Canal st", "building" : 21 } { "_id" : 2, "street" : "Fulton st", "building" : 31 } { "_id" : 1, "street" : "43rd st", "building" : 229 }$dateFromParts示例:# Add 15 months to month date field: > db.address.aggregate([ { $addFields: { next_visit: { $convert:{ input: { $dateFromParts: { year: "$last_visited.year", month: {$add:[15, "$last_visited.month"]}, }}, to: "date", onNull: "", onError: "" } } } } ]); { "_id" : 0, "street" : "Canal st", "building" : NumberDecimal("21.0000000000000"), "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 1, "street" : "43rd st", "building" : "229", "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 2, "street" : "Fulton st", "building" : "31", "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 3, "street" : "52nd st", "building" : "11w", "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 4, "street" : "78th st", "building" : null, "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 5, "street" : "78th st", "next_visit" : "" } { "_id" : 6, "street" : "Rector st", "building" : 10, "last_visited" : { "year" : 2017, "month" : 10 }, "next_visit" : ISODate("2019-01-01T00:00:00Z") }$trim示例:# conversion error: > db.address.aggregate( [ { $addFields: { building: {$convert: { input: "$building", to: "int" }} } }, {$sort: {building: 1}} ]); Error: command failed: { "ok" : 0, "errmsg" : "Failed to parse number '11w' in $convert with no onError value: Bad digit \"w\" while parsing 11w", "code" : 241, "codeName" : "ConversionFailure" } : aggregate failed # avoid conversion error: Using $trim expression with longer list of chars to remove: > db.address.aggregate( [ {$match: { building: {$type: "string"} }}, { $addFields: { building: { $convert: { input: {$trim: { input: "$building", chars: "abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz "}}, to: "int" } } } }, {$sort: {building: 1}} ]); { "_id" : 3, "street" : "52nd st", "building" : 11 } { "_id" : 2, "street" : "Fulton st", "building" : 31 } { "_id" : 1, "street" : "43rd st", "building" : 229 }
- 可结合:
修改订阅扩展
- 3.6 集合层面的修改订阅
- 4.0 数据库/集群层面的修改订阅(为修改事件返回clusterTime)
后备节点读取: 阻塞 -> 非阻塞性(引入快照机制)
- 阻塞性后备节点:
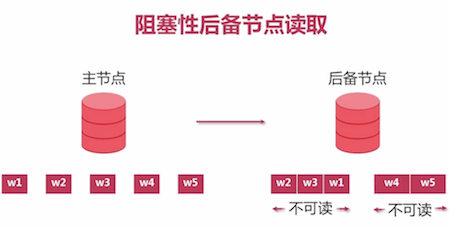

- 读取:需等待批量数据复制写入操作完成才可
- 写入: 需等待数据读取操作完成,否则会导致一致性问题
- 形成了一个恶性循环
- 非阻塞性后备节点:
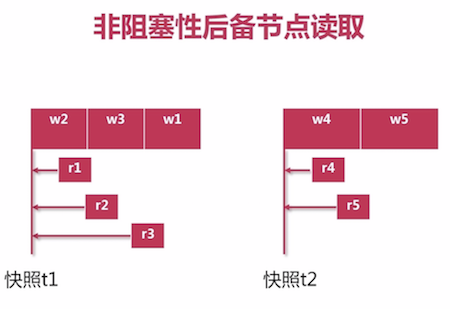
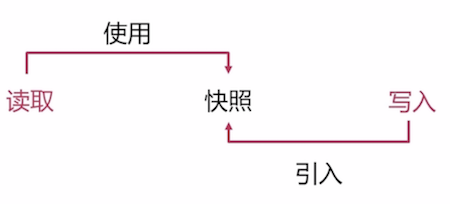
- 改进优化了性能:
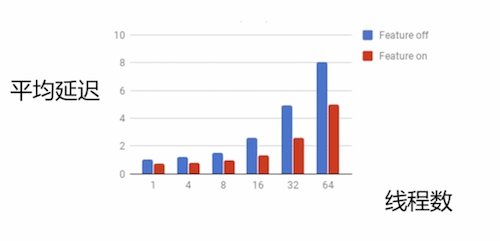
- 阻塞性后备节点:
Application
- Java:
mongodb-driver- Refer MongoDB Java
- Demo java-mongo
- NodeJS:
mongoose- Refer mongoose
- Demo node-mongo
Reference
MongoDB 3.4 中文文档 MongoDB 4.0 Manual MongoDB 教程 『浅入浅出』MongoDB 和 WiredTiger